Look: My little old Behringer Eurorack MX1604A mixing console has four insert jacks now, just what you need for a four-channel compressor. After a day spent with sick kids, a little soldering and drilling felt just right.
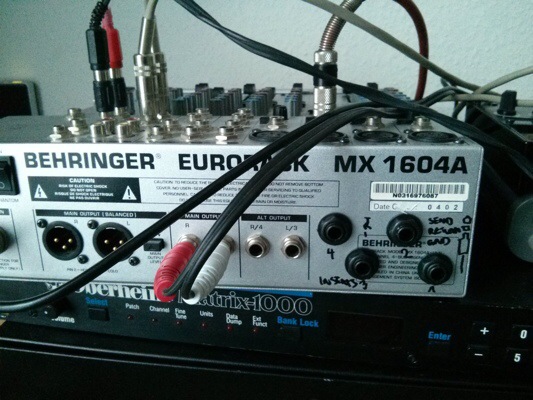

I have been shopping on eBay. Looking for a reverb to go with my rediscovered Oberheim Matrix synth, I acquired a rack containing a Lexicon MX, and a four-channel compressor. Lucky me.
This is when I noted that my mixer has no inserts.
Well, I fixed it. Took me about 3 hours. You need: 4 6.3mm stereo jacks, shielded 3-wire cables, soldering iron and being prepared to use it, a 12mm steel drill.
Category Archives: Musik
I’ve put my modded IO Dock on eBay!
It’s the first ever IO Dock outside Alesis’ labs to feature a USB hub, it’s the most successful project in this blog, and I am selling it. 
It was a simple hack on a crazy notion, and I’m really happy how it all turned out, getting noted by Discchord and Synthopia and others. More importantly, it’s a simple solution for a real problem, and it just works.
I’m also a lot more confident that it’s a good hack: The modified IO Dock has been in use at home and in the band for over a year, and the hack has been successfully replicated by some very smart hackers – over at Churchnerd’s blog you’ll not only find a description how to do it that is way better than mine, he also found a simple and elegant way to make the modded dock work with the iPad Air.
So why am I selling? I’ve got a good reason: Money. :) Apart from that, I am using an iPad Air now and switched over to another interface – a third-hand Novation X-Station keyboard/synth/fx combi with class-compliant USB Midi and Audio in/out. Best solution in the practice room for the time being, and if I’m getting a good price on my IO Dock, I might go out and get a Focusrite iTrack Dock to use at home.
However, I encourage you to try the hack for yourself, and I am confident that it will work with the new, lightning connector enabled, IO Dock 2. (Update: unfortunately, it doesn’t.)
A couple of things I have learned:
- Some people are really scared by the bullshit warnings that advise you not to open the housing.
- Anybody who can solder a cable can do it.
- The hub matters. I was lucky to pick an active hub that works in my setup, a Belkin F5U404. If the hack does not work, and you have excluded switched in/out ports and messed-up USB connections as the cause, you may try another powered hub.
- Use connectors, don’t solder it into the IO Dock – although you need 2mm pinstripe plugs/sockets like these that may be a bit hard to find, it is worth the effort: you’ll be able to test and reverse the hack.
- Lab-test first. Dremel later. Before soldering or dremeling anything in the Dock, start with a simple workbench test – open the Dock, unplug the connector for the iPad, connect it to the hub with the modified cables you’ve made.
- If you overload the IO Dock by drawing too much USB current, it just shuts down. So far, no harm has been done, still I think it’s a good idea to be careful and never connect more than one 500mA device.
- When you are hacking the IO Dock anyway, you might think about adding a power-on LED connected to the hub’s 5V supply – I always regretted not having done this.
One thing left to do: Many, many thanks for all the feedback, the ideas and the improvement. It made it all worth while. Whatever the turnout of my auction is.
Matrix Modulation control included: iPad editor for the Oberheim Matrix-6/1000
Remember what I wrote about my attempt to build an iPad editor for my vintage Matrix-1000 analog synth with TB Midi Stuff? That it’s a pity that, due to the rather eccentric MIDI implementation of the Oberheim machine, I couldn’t build a controller for the modulation matrix? Tell you what: it works now.

TB Midi Stuff – which is an absolutely great universal kit for building MIDI controllers, looking great and much cheaper than Lemur – has recently gained a feature that allows to send three-variable Sysex commands. And this is important – let me tell you why. (BTW, for those who can’t wait: Download links to the Matrix-1000 editor panels can be found in the TMBS forum. [here – v1.03, “Open with…” TBMS on the iPad])
Update, January 2022: TB Midi Stuff has been pretty much abandonware for years now; although you can still use – and buy – it, it is more and more at odds with newer iOS versions. Use at your own risk. And you might try badgering Fabien Manchec, the developer, about his promise of an update from mid-2020, but be kind – solo developers don’t make a fortune on those niche apps.
Let me explain the problem, and how to solve it with TBMS.
Unfortunately, this won’t work with Matrix-6s – they do not understand the sysex commands needed to program the mod matrix directly.
The Oberheim’s matrix control – one command, three parameters
As I’ve written before, the Oberheim Matrix-1000 has a couple of quirks and issues, especially concerning the modulation matrix, the analog synth’s strongest asset. Almost any other sound parameter within this synth can be controlled individually with a tailored MIDI Sysex message (something like: F0 10 06 06 1A xx F7, translating as “Listen synth, control coming up, setting vcf, to VALUE, thatsit”); the matrix modulation paths are set by a command sequence like this: F0 10 06 0B 01 xx yy zz F7, translating to “Listen synth, modulation coming up, setting modulation path 1 now, FROM, BY, TO, thatsit.” What this means is: If you want to have full control over the modulation matrix, you have to be able to craft a Sysex message with at least three parameters.)
TBMS from version 2.2.4 on has a feature to achieve this: Masked variables – variables where you can set the bits you want to control. They can be up to 21 bits large – equalling three 7-bit MIDI values. So instead of sending three independent values, you tell TBMS how to craft a 21-bit variable containing the three parameters – and send this.
Step by step:
-
- Define a global variable by entering Edit mode, selecting Page Settings in the upper right corner, scrolling down all the way, and adding a user variable. I’ve called it “mod0”, for modulation path 0; I’ve made it an internal variable, don’t worry about assigning it a range and max and min values for now.
- Now, define a controller for the third of my three parameters – MIDI parameters are 7 bit only, e.g. between 0 and 127, equalling a hexadecimal value of 7F. Hexadecimal numbers are what you use in Sysex and masked variables, so what you do is add a Variable Message, select “Set Variable with Mask”, and set the mask to 7F. (My values are 0-32, so no setting the “Signed” switch for this parameter. Remember to set the “Minimum Value” and “Maximum Value” to 0 and 20.)
- Define a controller for the middle parameter – just as with the one above, only with a slight modification: Set the mask to 3F80. — Why is that? It’s 7F shifted left by 7 bits, and as you remember, parameters in MIDI are 7 bits. One noteworthy thing about the middle parameter: In my case, it takes values between -63 and +63, so I’ve set the “Signed” switch here and set the “Minimum” and “Maximum” sliders to -63 and +63.
- Only the most significant parameter missing now: Add another control for the first parameter, shift the mask by another 7 bit, and get 1FC000. Set Signed, Minimum and Maximum as desired (I used a 0-20 range here.)
- Go back to Edit mode, call up the Page Settings, scroll down to your user variable, and add a MIDI message to it: Make it a Sysex message. Set Variable Size to three-byte and – this is important – Message Format to Linear (Little Endian). “Little Endian” means that the lower values are sent first; as we’ve made our first controller control the lower 7 bits, this is just right. Set a Sysex message, which in my case is “(F0)10060Bxx(F7)”.
I guess there are not that many people who have followed my that far – but if you have, you may have noticed that the variable is supposed to transmit 3*7=21 bits of information, resulting in an integer range of 0 to 2,097,151. You can actually set that value in the Sysex range control setting,.
So whenever you tweak the controls for Matrix modulation path 0, TBMS constructs a three-byte, 21-bit message, which it then sends as part of a Sysex control message.
Enjoy!
The most recent version can be found in the TBMS forum. Dropbox link to V0.4 here and here. Please remember that there are two nasty bugs in the Matrix-1000 firmware – you cannot control ENV2->VCA and ENV1 Sustain via TBMS in consequence -, and that the editor only sends Sysex, it does not receive and interpret it.
Reclaiming the Matrix: new life for an old beast via iPad control
Update: there is now a working editor template for editing Matrix-1000 sounds via the iPad with TB Midi Stuff. Other than stated below, it is now possible to control the modulation matrix as well – read more about it here. The buggy parameters unfortunately still won’t work.
I’m just rediscovering a 25-year old piece of analog hardware: my Oberheim Matrix-1000 synth. It’s worth rediscovering: The analog circuitry is still cutting through any mix; it’s a nasty classic. And it’s a simple 1 HU 19” rack unit; power supply included, no wall warts.
So yes, for a vintage piece of equipment, it’s handy. Unfortunately, the Matrix-1000 is a pure expander module without a single controller – no real-time tweaking the sounds to your desire. Which is a massive disadvantage to an otherwise extremely clever and versatile machine, as I’m not the first to discover. Before Access started to make very expensive top-quality VA synths, they did a hardware controller; you’ll occasionally find one on eBay for around € 700. Translating as: “It’s a monster if you can only get a controller for it.”

My favourite digital music device is the iPad. So I’ve started making my own iPad controller interface, based on the cheap TB Midi Stuff controller kit. It’s an early version, still some testing to be done. And there’s a couple of things you need to realize about the Matrix-1000 before using it with an external editor.
iPad Air: Shut up and take my money!
Yes, I know. We’re all a bit disappointed with the “New New New iPad”, a.k.a. iPad Air. And remember what Apple pulled off when they discovered that they had a game-changing new component, the Retina display, but the overall hardware wasn’t up to the level yet – they sold it as the iPad 3, only to be replaced with the iPad 4 less than a year later.
No, I’m not bitter with Apple over that. Well yes, I am, but the problem with my iPad 3 is that processing power has become an issue when using it for making music – an important use case for me. Waldorf’s Nave is a dream of a soft synth, but it’s pushing my iPad to the limit – run Nave, and you won’t be able to run much else. So processing power is increasingly becoming the driving force in deciding on what to buy and when.
The least thing that you could say about the iPad Air is that it’s going to drive down the prices for iPad 4’s. But considered that the Air is sporting a variant of the last-generation Apple A7 processor, you can expect it to have about double the processing power of an iPad 4, or about six times the performance of the iPad 3. That’s presumably worth a hundred Euros extra.
To get rid of the iPad3 now might be a good idea anyway. See Tim Webb’s analysis over at Discchord:
The iPad 3 shipped with an inferior processor incapable of keeping up with the huge retina display, and suffered a life-time of sluggish performance and annoying bugs. Developers consistently tell me that the majority of their bug reports come from iPad 3 users.
Now there you go. Unfortunately, this means that my carefully hand-modded IO Dock becomes obsolete – the iPad Air, due to its smaller bezel and different overall dimensions, just won’t fit, and there’s the issue of the Lightning connector which the IO Dock doesn’t have – although there are reports that an adapter would work, this would mean additional tinkering, soldering, dremeling. With hardly any chance of producing satisfactory results.
So what I’ll probably do is build a USB setup from scratch, with a modded Lightning-to-USB-adapter capable of charging the iPad; maybe with a powered hub, and a multi-channel interface like the Akai EIE. (Good list of class-compatible, iPad-friendly devices here.) It’s far from perfect, and maybe sometime I’ll integrate it into my own Dock. Once again, terra incognita.
Hammerhacks: Das gehaltene iPad und das verschwundene Keyboard
Ist noch gar nicht so lange her, da sah meine gemütliche kleine Krachmacherecke zuhause in etwa so aus:
Dann kam so nach und nach noch ein wenig was dazu: ein Hardware-Synthesizer, das IO Dock und ein IKEA-“Lack-Rack”-Style-Schränkchen für den HiFi-Receiver. Und ich sah, dass es gut war.
Doch auf einmal ist die ehemalige KRachmacherecke nahezu unheimlich – ähem – gemütlich:
Was ist passiert? Musste die Technikzone verschwinden, weil sie die WAF-Grenzwerte gerissen hat? Ja und nein – Antwort nach dem Klick. Continue reading
Give me a hand: Looking for the perfect iPad Beatbox companion
 I love Loopy. The nifty little looper program by this mad Australian guy has become the fourth member in our little band project; it looks gorgeous, it works flawlessly, and it’s so simple to use: Just load any rhythm loop into Loopy, auto-stretch the sample to time, record additional audio or loop live, switch between loops with MIDI PC commands – which my FCB1010 foot controller is happy to supply.
I love Loopy. The nifty little looper program by this mad Australian guy has become the fourth member in our little band project; it looks gorgeous, it works flawlessly, and it’s so simple to use: Just load any rhythm loop into Loopy, auto-stretch the sample to time, record additional audio or loop live, switch between loops with MIDI PC commands – which my FCB1010 foot controller is happy to supply.
You need additional tools, though. Loops coming from my favourite beatbox have to be post-processed for dynamics and overall punch. And playing around with the free Launchpad app by Novation got me thinking. What Loopy doesn’t do, though: just trigger loops and samples. And songs have to stick to a very rigid timing grid, normally 4 bars; otherwise you’d switch loops just in the middle of your chorus track.
Organic Proto-Beatbox Band
Why bother? Why not just use Ableton Live or, if you want to spare yourself having to drag a laptop around, buy some dedicated hardware? An Akai MPC, a Roland SP-404, an Electribe, or: Bloody hell – just use whatever sampler groovebox you like.
Which is what I’m going to do, only that I’d like to buy it as an app. Everything stays in my iPad, another advantage being that due to perversity of the app store economy, software is usually a fraction of the price of more traditional solutions. (Which is why we will probably never see an iOS version of Ableton Live.)
So just pop over to the app store and just find a sample-based, loop-based beatbox app. Can’t be that hard to do, no? It is. A friendly way to describe the abundance of music apps would be “very rich organic growth”. So many programmers and small companies have started their own music apps, which is a great thing. Sadly, hardly any of them get it right.
Looking for the perfect companion
It’s easy enough to name what I am looking for:
- A simple live-playing mode similar to Ableton Live or an MPC
- Different trigger modes: one-shot and loop-based
- Ability to import and export loops
- Time-stretching
- App has to work in the background
- Has to be controllable via MIDI
On top of that, Audiobus. And a couple of simple processing tools would be nice.
Google didn’t help much. So I started a table, which is far from comprehensive, but I’m opening up it for you to supply additional information.
This is what has been found so far:
My favourites so far? Most apps by traditional music hardware manufacturers seem to be severely limited, their main object being a marketing tool for in-app purchases. I’d go for Protein Der Klang, but it doesn’t have MIDI. So I’d settle for Beatmaker although I fear that it is too large and too complex.
So if YOU’d like to give me a hand, and know a thing about beatboxes or two, help to make this table useful by supplying additional info. (Just follow this link to the Google Doc). I suggest keeping discussions and opinions to the comments (in the table and in this post) and keep the table to facts-only.
QuNexus: Kein Hack, ein Tipp…
…wer eine Tasche sucht und bei den DJs und im Computerladen nicht fündig wird: Querflötentaschen passen! (Es muss ja nicht die mit dem Hermelinsackhaarsamtfutteral sein.)
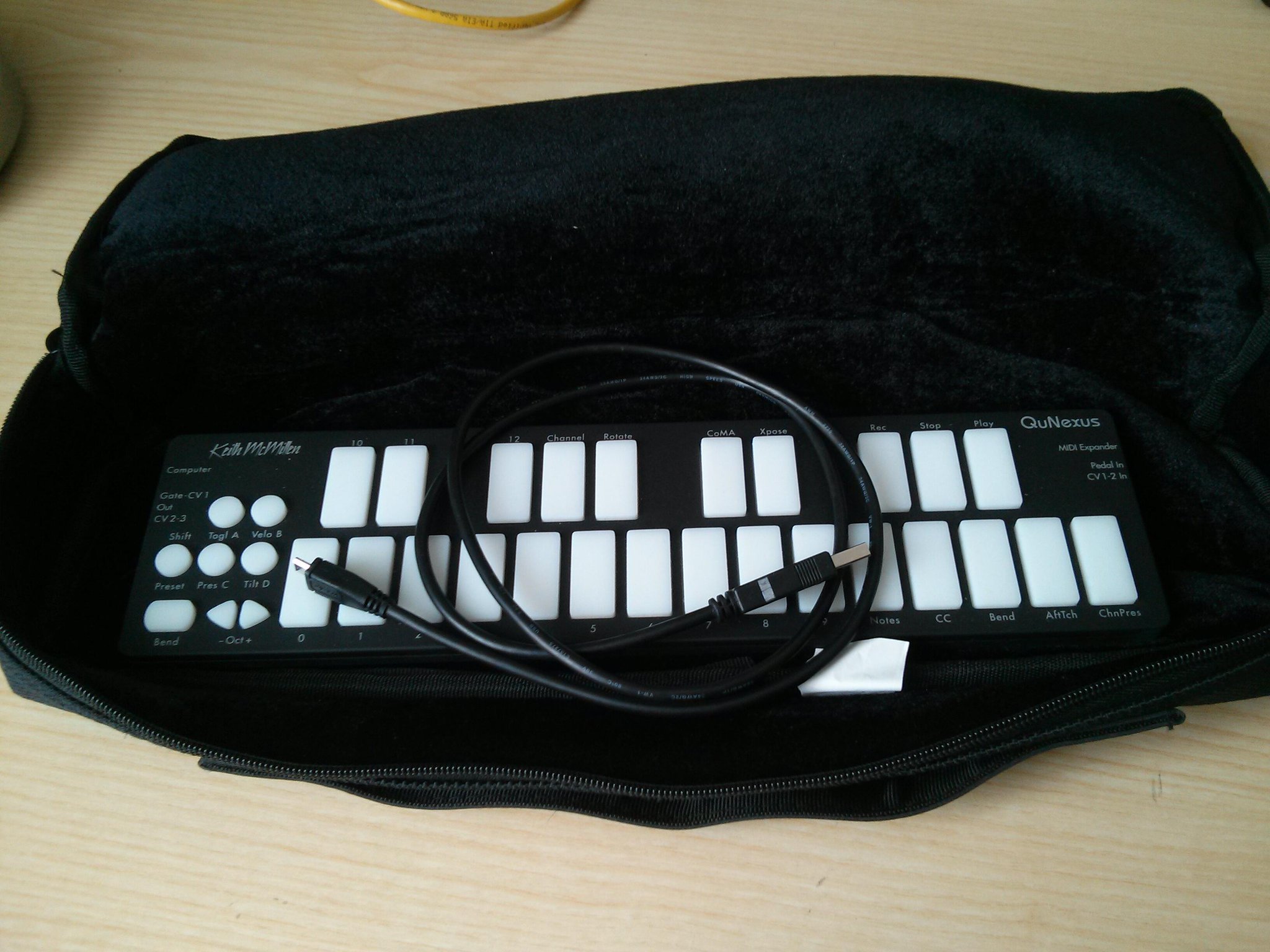

QuNexus in einer billigen Querföltentasche chinesischer Provenienz.
Ansonsten: Der QuNexus hat inzwischen einen deutlichen Versionssprung gemacht – und demnächst wird sich hoffentlich mal Zeit finden, die Analogausgänge auszutesten. Mit einem Korg Monotron Duo! Muhahaha!
Change, the old way
Back in the Space Age, when they first invented MIDI, synths and drum machines used to have 8-bit processors with a measly 64k memory address range (as in 64kByte, you snotty, spoiled digital age brats). Usually that allowed them to store a couple of different presets, say: 16 or 32, so it wasn’t really a problem that the command for switching between presets – appropiately named PC, Program Change – could only transfer values between 0 and 127. (7 bit – it’s a MIDI thing.) But time moved on: Memory grew cheaper and cheaper, and machines gathered more and more preset slots. Presumably, a drum machine with 512 factory presets sold much better than its older sibling with 32 preset slots – it has always been easy to impress customers with numbers. PC still only transmitted the 0-127 range, but it became standard to use the two Midi controllers CC0 and CC32 to transmit a two-byte bank number, so now there was, in theory, the possibility to address 2^21 = 2,097,152 different presets. Everybody happy, case closed.
In theory.
Yet, a lot of people never bothered with this tedious CC/Bank Change business. Who ever needed more than a handful of presets on stage? To this day, you can buy quite sensible MIDI devices that don’t understand anything other than the ancient MIDI PC command, my trusted Behringer pedalboard is a case to the point. (BTW: I can recommend upgrading it with a quite ingenious unofficial firmware upgrade, which does a lot, but still does not offer Bank Change.) And this is where this story actually starts.
Did I mention how it infuriates me when modern iPad apps do not seem to know MIDI? OK, I did, and to be honest, with most of the apps, it proved to be more of a “banana software” problem – the app just needed more time with the customer to ripe. So I was not really surprised when I ran into problems with my two favourite softsynths, only a little disappointed. The all-new, all-shiny, all-mindbending Waldorf Nave app deserves to be mentioned first; using PC commands, you can only change between the sounds in the first bank of factory presets, and you cannot store anything there. Support acknowledges that this is a problem and promises, in an e-mail to me, that future releases are going to bring an “Assign preset to PC” feature.
It has not been quite that much of an issue with Sunrizer: everbody’s second-best soft synth always allowed you to save sounds to the first bank, so you could pretty much prepare what you needed. Until Beepstreet did an update that brought a new look, very Polysixish and, if you ask me, drop dead ugly. And a a new bank of presets named AI. A new first bank of sounds. Back to square one.
The Sunrizer Bank Hack
I must admit that I wasn’t amused at all. Yet the solution is quite simple, and after letting of some steam even I saw it. This is what you should do:
- Store all your performance presets in a new user bank.
- Connect your iPad to iTunes.
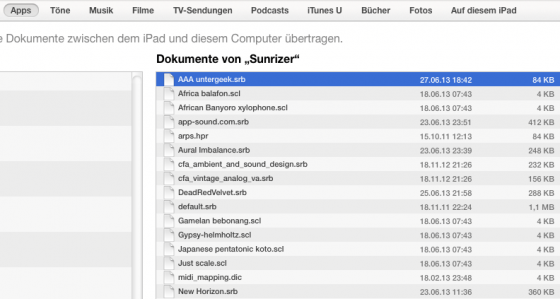
- Select Apps, scroll down to the section where you can transfer files to/from apps. Select Sunrizer.
- Find your bank of performance sounds (it’s a file called something.srb).
- Klick it and rename it to “AAA performance.srb”. (Alphabetically, it’s now the first bank, you see.)
- Sync the iPad again.
- On the iPad, close and restart the Sunrizer app. If you don’t know how to do this, switch off and restart the iPad.
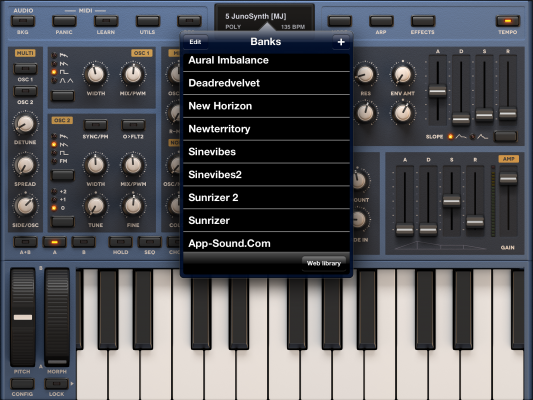
 This simple operation makes your bank of custom presets the first bank in memory, and the first place you’ll be reaching by sending Sunrizer a PC command. I’ve tried. You still have to count presets to get to the right one – but I’m pretty confident we will cope, you and I.
This simple operation makes your bank of custom presets the first bank in memory, and the first place you’ll be reaching by sending Sunrizer a PC command. I’ve tried. You still have to count presets to get to the right one – but I’m pretty confident we will cope, you and I.
There it is, a tinkerer’s legacy: Change, the old way.
QuNexus: Das Griffbrett für den aufstrebenden iPad-Synthesisten
Update. 27.6.13: Nicht nur, dass Keith McMillen innerhalb von Stunden auf meinen Bugreport reagiert hat, das in der Antwort angekündigte Update ist inzwischen draußen – der Editor V1.1 behebt die bemängelten Schwächen.
Frisch von Kickstarter: Gerade ist mein Exemplar aus der ersten Serie QuNexus-Keyboard-Controller von Keith McMillen eingetroffen. Echt klein – und fühlt sich trotz all dem Plastik nicht billig an, sondern solide und wertig. Alles, was man braucht, um mit dem iPad Musik zu machen – das Camera Connection Kit und ein paar tolle Softsynths wie Sunrizer, Magellan oder (ganz neu! ganz heiß!) der Waldorf Nave liegen ja ohnehin in jedem besseren Soundbastlerhaushalt herum.
 Größenvergleich: Der komplette QuNexus würde glatt 4x auf die Fläche meines M-Audio Axiom 25 passen. Und ist dabei deutlich leichter zu transportieren und zu programmieren.
Größenvergleich: Der komplette QuNexus würde glatt 4x auf die Fläche meines M-Audio Axiom 25 passen. Und ist dabei deutlich leichter zu transportieren und zu programmieren.Alles da, was man braucht also – vorausgesetzt, man kommt mit den frickeligen Minitasten zurecht und findet die richtige Kombination aus QuNexus-Programmierung und Synthesizer-Sound.
Portabler Altar für Tastengötter
Vor vielen, vielen Jahren, ich war noch deutlich jünger, da träumte ich von einem Chapman Stick. (Es waren gerade noch die verdammten 80er, you see.) Zum Glück habe ich mir nie einen angeschafft, denn für jemanden wie mich – einen handwerklichen Dilettanten mit großer Experimentierfreude, aber immer zu wenig Zeit und zu wenig Lust zum Üben – wäre es genau das falsche Instrument gewesen. Ich hege den Verdacht, dass es mit dem QuNexus genauso sein könnte; die Anordnung der Tasten ist ähnlich wie bei einer Klaviertastatur, aber meine Finger finden sich einfach nicht zurecht. Da ist viel Übung gefragt.
Vermutlich hat Keith beim Kalibrieren des QuNexus auch an kräftigere Finger gedacht als die meinen, denn ich schaffe es auch mit größter Kraftanwendung nicht, den Dynamikumfang der Anschläge und der Aftertouch-Funktion auszuschöpfen. Ein Midi-Monitor bestätigt meinen Verdacht: Werte über 107, 108 sind nicht zu erreichen. (Allerdings kann man da mit dem Editor nachjustieren und andere Dynamikkurven, Schwellen und Verstärkungen einstellen.)
Der Editor: Mehr als eine v1.0 gebe ich ihm nicht
Womit wir beim Editor wären, meines Erachtens derzeit der größte Schwachpunkt des QuNexus. So wie er sich auf meinem Netbook gibt, scheint er fest für die Bildschirmauflösung 1024×768 konzipiert zu sein – der deutlich höher auflösende 10”-Bildschirm meines Samsung NF310 ist nur etwa zu einem Viertel gefüllt, was für die Lesbarkeit nicht gerade optimal ist. Und er gibt mehr Flexibilität vor, als er tatsächlich ermöglicht.
 Der QuNexus-Editor v1.0.1: Screenshot bei 1366×768
Der QuNexus-Editor v1.0.1: Screenshot bei 1366×768Gut, man kann Empfindlichkeit und Dynamikverlauf einstellen und die Parameter Druck und Druckpunkt den üblichen Midi-Controllern zuweisen. Gedacht ist das für die Standard-Synthesizer-Controller: Schwächerer oder stärkerer Druck auf die Taste ersetzt das Modulationsrad, der Druckpunkt (ob man die Taste am vorderen oder hinteren Rand drückt) dreht an der Tonhöhe – wie ein Pitchrad, wobei der QuNexus mit einem Trick auch polyphon pitchen kann: wenn man will, wird jeder Tastendruck auf einem eigenen Midi-Channel übertragen, was ermöglicht, jede Stimme unabhängig von den anderen zu verbiegen.
Ein paar Wünsche bleiben – zumindest bei mir – offen:
- Ich würde gerne das “Bend”-Pad unten links frei belegen können – und nicht nur als Pitchwheel-Ersatz nutzen. Zum Beispiel als Modulationsrad.
- Es hat keinen Sinn, den “Tilt”-(Druckpunkt-)Parameter auf jeden Midicontroller legen zu können, wenn man den Nullpunkt nicht richtig bestimmen kann. Tilt für CC 1 (Modulationsrad) – nicht brauchbar, weil der Controller die Mittelstellung überträgt. Man könnte sich noch helfen, wenn man dem Editor einen Offset von -64 angeben würde, so dass die Nullstellung auch wirklicn 0 überträgt, aber leider kann man für den Offset keine negativen Werte eingeben.
- Sowieso: Warum nicht Druck vorne für Modulation, Druck hinten für einen anderen Midi-CC?
- Man kann einen Parameter immer nur einmal zuweisen – wäre aber schön, wenn man über den Druck sowohl Channel- als auch polyphonen Aftertouch steuern könnte.
Soweit meine paar Kritikpunkte; ich bin fast überzeugt, die Software wird reifen. Und ich werde üben. Und die nächste Bastelei steht auch schon fest: mal einen alten analogen Joystick suchen – und dann einen kleinen X-Y-Controller an den Eingang für die beiden Fußpedale anschließen…
Hier mein Unboxing-Video (auf englisch).